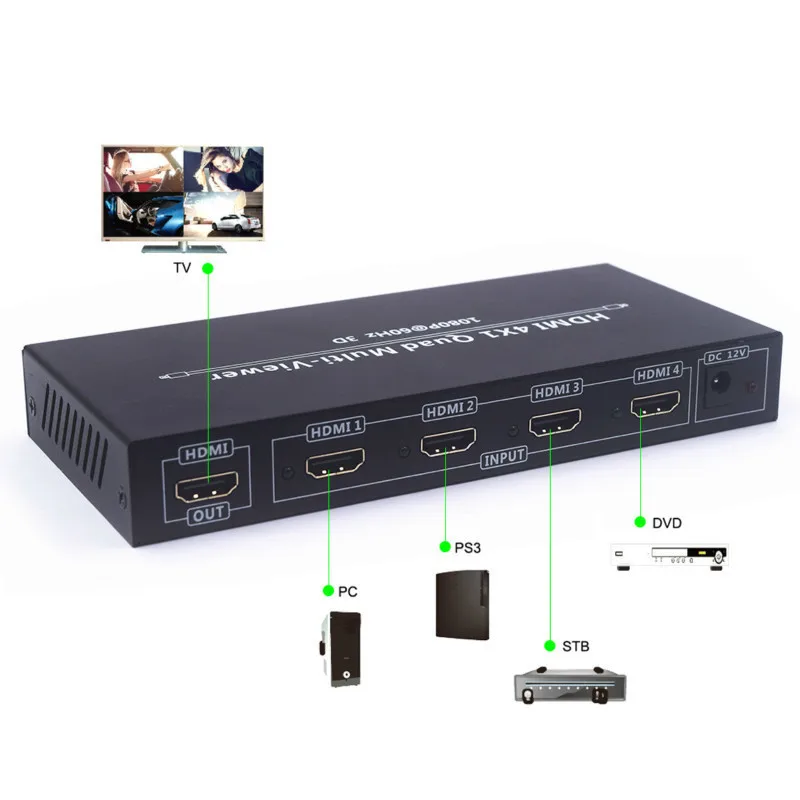


Therefore, this method is only meant for monitors whose resolutions are not available in the Video-Mode Method. This method is more involved and requires knowledge of all timing parameters for the desired resolution. The last method for setting the screen resolution also uses nvedit. If all of the previously described methods fail for your configuration, it is possible to specify the exact timing numbers for a particular resolution. Without these lines, the changes you make with nvedit will be ignored. The last three commands enable the NVRAM. See "Using nvedit to Modify NVRAM" for a description of nvedit commands.įor example, to set the screen resolution to 1024 x 768 at 60Hz, video-mode 8, type:

Use video modes 0-25 to select a screen depth of 24 bits, or video modes 26-33 to select a screen depth of 8 bits. These resolution settings are identified by video modes 0-33 ( Table 6-3).
The new screen resolution will take effect following the reset, and will hold the resolution information until the output-device variable is changed manually.Īt the ok prompt in Boot PROM mode, the screen resolution can be easily set on the PGX32 cards by using one of the 34 preinstalled resolution modes. Ok setenv output-device screen:r1024x768x75 The system will check these values against an internal list of resolutions (see Table 6-3), and use the corresponding entry as the screen resolution.įor example, to use VESA1024 x 768 at 75 as the screen resolution, type the following at the ok prompt: It is possible to specify the screen resolution of PGX32 card via the output-device environment variable by using the format screen:rAxBxC, where: A is the desired horizontal resolution, B is the desired vertical resolution, and C is the desired refresh rate. The methods described in this appendix will override any information obtained via EDID. The monitor must be turned on prior to booting the system in order for the PGX32 to communicate with it. Failing the above method, the card will default to 1152 x 900 x 66. With this protocol, the GFX card first checks the Standard Timing Identifiers (taking the first one supported), then tries to match the Established Timings. If you are using a monitor with DDC2B/EDID protocol, the default resolution will be determined using the Auto-Detect feature. The procedures for changing the screen resolution described in this chapter include: Use GFXconfig -i to test a resolution before configuring the screen to that resolution. Higher resolutions will default to 8-bit mode.
#Monitor resolution switcher windows#
To run the X Windows environment in 8/24 mode, set the screen resolution to 24 bit-depth.īy default, screen resolutions 1280 x 1024 and lower will automatically be set to 24 bit. The general guidelines to follow when changing the default screen resolutions are: The monitor does not "sync up" at the default screen resolution, then you need to choose a different screen resolution. You change the X Windows depth from the default listed in the table, then you should configure the screen depth to match the X Windows depth. However, you may need to change the default resolution if: Normally, the default screen resolution is sufficient for most users. Other Methods for Changing the Screen Resolution


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
